
Human Eye and Colourful World MCQ
1. A person cannot see distinctly objects kept beyond 2 m. This defect can be
corrected by using a lens of power
(a) + 0.5 D
(b) – 0.5 D
(c) + 0.2 D
(d) – 0.2 D
Ans. (b) -0.5 D
Explanation: This person is suffering from myopia. He needs a concave lens and
hence power would be in negative.
P = 1 /f = 1/2m =0.5D
2. A student sitting on the last bench can read the letters written on the
blackboard but is not able to read the letters written in his text book. Which
of the following statements is correct?
(a) The near point of his eyes has receded away
(b) The near point of his eyes has come closer to him
(c) The far point of his eyes has come closer to him
(d) The far point of his eyes has receded away
Ans. (a) The near point of his eyes has receded away
Explanation: In hypermetropia the near point of eye moves away from 25cm. Due to
this, the person needs to keep a book at more than 25 cm to read it properly.
3. A prism ABC (with BC as base) is placed in different orientations. A narrow beam of white light is incident on the prism as shown in Figure 11.1. In which of the following cases, after dispersion, the third colour from the top corresponds to the colour of the sky?
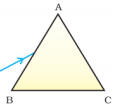
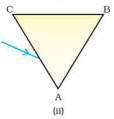
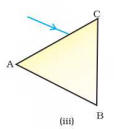
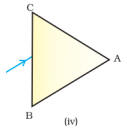
(a) (i)
(b) (ii)
(c) (iii)
(d) (iv)
Ans. (b) (ii)
Explanation: If prism is kept with base BC at bottom, then the emergent band of
colour would show violet at the bottom. If prism is kept with base BC at top,
then violet would be at top; followed by indigo and blue.
4. At noon the sun appears white as
(a) light is least scattered
(b) all the colours of the white light are scattered away
(c) blue colour is scattered the most
(d) red colour is scattered the most
Ans. (b) all the colours of the white light are scattered away
Explanation: Sky will appear dark in case of option ‘a’. It will appear blue in
case of option ‘c’ and will appear red in case of option ‘d’.
5. Which of the following phenomena of light are involved in the formation of a
rainbow?
(a) Reflection, refraction and dispersion
(b) Refraction, dispersion and total internal reflection
(c) Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection
(d) Dispersion, scattering and total internal reflection
Ans. (c) Refraction, dispersion and internal reflection
Explanation: Dispersion results in white light getting segregated into its
component colours. Refraction bends the incident light to an angle that is
causes internal reflection; and finally rainbow is formed.
6. Twinkling of stars is due to atmospheric
(a) dispersion of light by water droplets
(b) refraction of light by different layers of varying refractive indices
(c) scattering of light by dust particles
(d) internal reflection of light by clouds
Ans. (b) refraction of light by different layers of varying refractive indices
Explanation: Due to refraction of light by different layers of varying
refractive indices, the apparent position of source of light keeps on changing.
Due to this, stars appear to twinkle.
7. The clear sky appears blue because
(a) blue light gets absorbed in the atmosphere
(b) ultraviolet radiations are absorbed in the atmosphere
(c) violet and blue lights get scattered more than lights of all other colours
by the atmosphere
(d) light of all other colours is scattered more than the violet an blue colour
lights by the atmosphere
Ans. (c) violet and blue light get scattered more than lights of all other
colours by the atmosphere
8. Which of the following statements is correct regarding the propagation of
light of different colours of white light in air?
(a) Red light moves fastest
(b) Blue light moves faster than green light
(c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed
(d) Yellow light moves with the mean speed as that of the red and the violet
light
Ans. (c) All the colours of the white light move with the same speed
9. The danger signals installed at the top of tall buildings are red in colour.
These can be easily seen from a distance because among all other colours, the
red light
(a) is scattered the most by smoke or fog
(b) is scattered the least by smoke or fog
(c) is absorbed the most by smoke or fog
(d) moves fastest in air
Ans. (b) is scattered the least by smoke or fog
10. Which of the following phenomena contributes significantly to the reddish
appearance of the sun at sunrise or sunset?
(a) Dispersion of light
(b) Scattering of light
(c) Total internal reflection of light
(d) Reflection of light from the earth
Ans. (b) Scattering of light
Explanation: Red colour scatters the least and hence travels the farthest.
During sunset or sunrise, light has to travel a longer distance to reach us.
Hence, only red light reaches to us and the sky appears reddish.
11. The bluish colour of water in deep sea is due to
(a) the presence of algae and other plants found in water
(b) reflection of sky in water
(c) scattering of light
(d) absorption of light by the sea
Ans. (b) Reflection of sky in water
Explanation: Water is colourless. Its colour appears to be same as the object
reflected by it.
12. When light rays enter the eye, most of the refraction occurs at the
(a) crystalline lens
(b) outer surface of the cornea
(c) iris
(d) pupil
Ans. (b) Outer surface of the cornea
13. The focal length of the eye lens increases when eye muscles
(a) are relaxed and lens becomes thinner
(b) contract and lens becomes thicker
(c) are relaxed and lens becomes thicker
(d) contract and lens becomes thinner
Ans. (a) are relaxes and lens becomes thinner
14. Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) A person with myopia can see distant objects clearly
(b) A person with hypermetropia can see nearby objects clearly
(c) A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly
(d) A person with hypermetropia cannot see distant objects clearly
Ans. (c) A person with myopia can see nearby objects clearly
Explanation: This is the reason; myopia is also known as near sightedness.