
Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
The structure of CH3Cl
is given below:
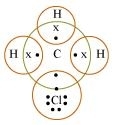
Carbon can neither lose four of its electrons nor gain four electrons as both
the processes require extra amount of energy and would make the system unstable.
Therefore, it completes its octet by sharing its four electrons with other
carbon atoms or with atoms of other elements. The bonds that are formed by
sharing electrons are known as covalent bonds. In covalent bonding, both the
atoms share the valence electrons, i.e., the shared electrons belong to the
valence shells of both the atoms.
Here, carbon requires 4 electrons to complete its octet, while each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete its duplet. Also, chlorine requires an electron to complete the octet. Therefore, all of these share the electrons and as a result, carbon forms 3 bonds with hydrogen and one with chlorine. The bond between C and Cl atoms is covalent but due to higher value of electro-negativity of Cl, the C�Cl bond is polar in nature.