
Show that if the diagonals of a quadrilateral are equal and bisect each other at right angles, then it is a square.
Given,
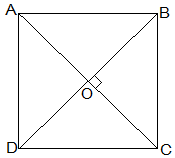
Let ABCD be a quadrilateral in which diagonals AC and BD bisect each other at right angle at O.
To prove,
Quadrilateral ABCD is a square.
Proof,
In ΔAOB and ΔCOD,
AO = CO (Diagonals bisect each other)
∠AOB = ∠COD (Vertically opposite)
OB = OD (Diagonals bisect each other)
Therefore, ΔAOB ≅ ΔCOD by SAS congruence condition.
Thus, AB = CD by CPCT. --- (i)
also,
∠OAB = ∠OCD (Alternate interior angles)
⇒ AB || CD
Now,
In ΔAOD and ΔCOD,
AO = CO (Diagonals bisect each other)
∠AOD = ∠COD (Vertically opposite)
OD = OD (Common)
Therefore, ΔAOD ≅ ΔCOD by SAS congruence condition.
Thus, AD = CD by CPCT. --- (ii)
also,
AD = BC and AD = CD
⇒ AD = BC = CD = AB --- (ii)
also, ∠ADC = ∠BCD by CPCT.
and ∠ADC + ∠BCD = 180° (co-interior angles)
⇒ 2∠ADC = 180°
⇒ ∠ADC = 90° --- (iii)
One of the interior ang is right angle.
Thus, from (i), (ii) and (iii) given quadrilateral ABCD is a square.