
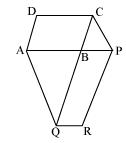
The side AB of a parallelogram ABCD is produced to any point P. A line through A and parallel to CP meets CB produced at Q and then parallelogram PBQR is completed (see Fig. 9.26).
The side AB of a parallelogram ABCD is produced to any point P. A line through A and parallel to CP meets CB produced at Q and then parallelogram PBQR is completed (see the following figure). Show that
ar (ABCD) = ar (PBQR).
[Hint: Join AC and PQ. Now compare area (ACQ) and area (APQ)]
Answer
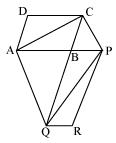
AC and PQ are joined.
ar(△ACQ) = ar(△APQ) (On the same base AQ and between the same parallel lines AQ and CP)
⇒ ar(△ACQ) - ar(△ABQ) = ar(△APQ) - ar(△ABQ)
⇒ ar(△ABC) = ar(△QBP) --- (i)
AC and QP are diagonals ABCD and PBQR. Thus,
ar(ABC) = 1/2 ar(ABCD) --- (ii)
ar(QBP) = 1/2 ar(PBQR) --- (iii)
From (ii) and (ii),
1/2 ar(ABCD) = 1/2 ar(PBQR)
⇒ ar(ABCD) = ar(PBQR)