
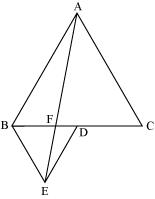
In the following figure, ABC and BDE are two equilateral triangles such that D is the mid-point of BC. If AE intersects BC at F, show that (iii) ar(ABC) = 2 ar(BEC)
In the following figure, ABC and BDE are two equilateral triangles such that D is the mid-point of BC. If AE intersects BC at F, show that
(iii) ar(ABC) = 2 ar(BEC)
ANSWER
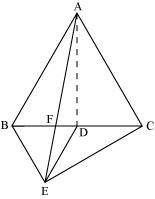
ar (ΔABE) = ar (ΔBEC) (Common base BE and BE||AC)
ar (ΔABF) + ar (ΔBEF) = ar (ΔBEC)
Using equation (1), we obtain
ar (ΔABF) + ar (ΔAFD) = ar (ΔBEC)
ar (ΔABD) = ar (ΔBEC)
1/2 ar(ΔABC) = ar(ΔBEC)
ar (ΔABC) = 2 ar (ΔBEC)