NCERT Solution: Carbon and its Compounds
The structure of CH3Cl
is given below:
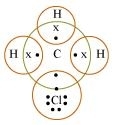
Carbon can neither lose four of its electrons nor gain four electrons as both
the processes require extra amount of energy and would make the system unstable.
Therefore, it completes its octet by sharing its four electrons with other
carbon atoms or with atoms of other elements. The bonds that are formed by
sharing electrons are known as covalent bonds. In covalent bonding, both the
atoms share the valence electrons, i.e., the shared electrons belong to the
valence shells of both the atoms.
Here, carbon requires 4 electrons to complete its octet, while each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete its duplet. Also, chlorine requires an electron to complete the octet. Therefore, all of these share the electrons and as a result, carbon forms 3 bonds with hydrogen and one with chlorine. The bond between C and Cl atoms is covalent but due to higher value of electro-negativity of Cl, the C�Cl bond is polar in nature.
(a) Ethanoic acid
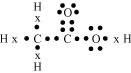
(b) H2S
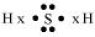
(c) Propanone
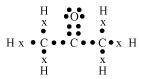
(d) F2
A homologous series is a series of carbon compounds that have different numbers of carbon atoms but contain the same functional group.
For example, methane, ethane, propane, butane, etc. are all part of the alkane homologous series. The general formula of this series is CnH2n+2.
Methane CH4
Ethane CH3CH3
Propane CH3CH2CH3
Butane CH3CH2CH2CH3
It can be noticed that there is a difference of -CH2 unit between each successive compound.
Ethanol and Ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their following properties:
→ Ethanol is a liquid at room temperature with a pleasant smell. Ethanoic acid has a melting point of 17�C. Since it is below the room temperature so, it freezes during winter. Moreover, ethanoic acid has a smell like vinegar.
→ Ethanol does not react with metal carbonates while, ethanoic acid reacts with metal carbonates to form salt, water and carbon dioxide. For example,
2CH3COOH + Na2CO3 → 2CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O
→ Ethanol does not react with NaOH while ethanoic acid reacts with NaOH to
form sodium ethanoate and water. For example,
CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O→ Ethanol is
oxidized to give ethanoic acid in presence of acidified KMnO4 while,
no reaction takes place with ethanoic acid in presence of acidified KMnO4.
Soap molecule has two ends. One end is hydrophilic and another end is hydrophobic. When soap is dissolved in water and clothes are put in the soapy solution, soap molecules converge in a typical fashion to make a structure; called micelle. The hydrophobic ends of different molecules surround a particle of grease and make the micelle; which is a spherical structure. In this, the hydrophilic end is outside the sphere and hydrophobic end is towards the centre of the sphere. This is why micelle formation takes place when soap is added to water.
Since ethanol is not as polar as soap, so micelles will not be formed in other solvents such as ethanol.
Carbon and its compounds give large amount of heat on combustion due to high percentage of carbon and hydrogen. Carbon compounds used as fuel have optimum ignition temperature with high calorific values and are easy to handle. Their combustion can e controlled. Therefore, carbon and its compounds are used as fuels.
Hard water often contains salts of calcium and magnesium. Soap molecules react with the salts of calcium and magnesium and form a precipitate. This precipitate begins floating as an off-white layer over water. This layer is called scum. Soaps lose their cleansing property in hard water because of formation of scum.
Since soap is basic in nature, it will turn red litmus blue. However, the colour of blue litmus will remain blue.