NCERT Solution: Carbon and its Compounds
Hydrogenation is the chemical reaction between hydrogen and other compounds in the presence of catalyst. Hydrogenation is used mainly to reduce saturated hydrocarbons. Hydrogenation is an addition reaction.For Example: When ethene is heated with the catalyst nickel it is reduced to ethane.
Industrial application:
→ >Hydrogenation is used in many industrial applications. For example; in Petrochemical Industry, hydrogenation is used to convert alkenes into alkanes (paraffins) and cycloalkanes.
→ It is also used to prepare vegetable ghee from vegetable oils.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions. Being unsaturated hydrocarbons, C3H6 and C2H2 undergo addition reactions.
Butter contains saturated fats. Therefore, it cannot be hydrogenated. On the other hand, oil has unsaturated fats. That is why it can be hydrogenated to saturated fats (solids).
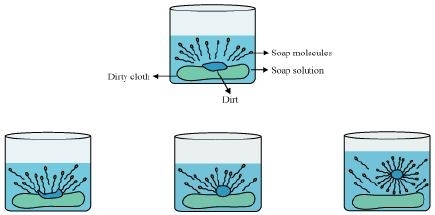
The dirt present on clothes is organic in nature and insoluble in water. Therefore, it cannot be removed by only washing with water. When soap is dissolved in water, its hydrophobic ends attach themselves to the dirt and remove it from the cloth. Then, the molecules of soap arrange themselves in micelle formation and trap the dirt at the centre of the cluster. These micelles remain suspended in the water. Hence, the dust particles are easily rinsed away by water.
Cleansing action of soaps
1. Carbon exists in the atmosphere in the form of
(a) carbon monoxide only
(b) carbon monoxide in traces and carbon dioxide
(c) carbon dioxide only
(d) coal
Ans. (c) carbon dioxide only
2. Which of the following statements are usually correct for carbon compounds? These
(i) are good conductors of electricity
(ii) are poor conductors of electricity
(iii) have strong forces of attraction between their molecules
(iv) do not have strong forces of attraction between their molecules
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans. (d) (ii) and (iv)
Explanation: Organic compound are made of covalent bonds. These bonds have weaker forces of attraction. Covalent compounds are poor conductors of electricity.
3. A molecule of ammonia (NH3) has
(a) only single bonds
(b) only double bonds
(c) only triple bonds
(d) two double bonds and one single bond
Ans. (a) Only single bonds
Explanation: The valency of nitrogen is 2 and that of hydrogen is one. Three atoms of hydrogen combine with 1 atom of nitrogen to make ammonia. Hence, there are three single bonds in ammonia.
4. Buckminsterfullerene is an allotropic form of
(a) phosphorus
(b) sulphur
(c) carbon
(d) tin
Ans. (c) Carbon
5. Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans. (c) (i) and (ii)
Explanation: Formula of butane is C4H10. Options (iii) and (iv) have 8 hydrogen atoms each, hence, they are incorrect.
6. In the given reaction, alkaline KMnO4 acts as
(a) reducing agent
(b) oxidising agent
(c) catalyst
(d) dehydrating agent
Ans. (b) Oxidising agent
Explanation: Two hydrogen atoms are replaced by an atom of oxygen in this reaction. This shows oxidization of ethanol. Addition oxygen is being provided by potassium permanganate.
7. Oils on treating with hydrogen in the presence of palladium or nickel catalyst form
fats. This is an example of
(a) Addition reaction
(b) Substitution reaction
(c) Displacement reaction
(d) Oxidation reaction
Ans. (a) Addition reaction
Explanation: In this reaction, hydrogen is added to oil.
8. In which of the following compounds, — OH is the functional group?
(a) Butanone
(b) Butanol
(c) Butanoic acid
(d) Butanal
Ans. (b) Butanol
Explanation: Compounds with -OH as functional group have ‘ol’ as suffix.
9. The soap molecule has a
(a) hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
(b) hydrophobic head and a hydrophilic tail
(c) hydrophobic head and a hydrophobic tail
(d) hydrophilic head and a hydrophilic tail
Ans. (a) Hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
Explanation: Oil and grease is trapped inside a micelle because of hydrophobic tail. Hydrophilic head makes the outer surface of micelle. Thus, a micelle is easily washed by water.
10. Which of the following is the correct representation of electron dot structure of nitrogen?
Ans. (d)
Explanation: In this structure, each nitrogen atom gets 8 electrons. This is not the case in other options.
11. Structural formula of ethyne is
Ans. (a)
Explanation: The formula of ethyne is C2H2.
12. Identify the unsaturated compounds from the following
(i) Propane
(ii) Propene
(iii) Propyne
(iv) Chloropropane
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Ans. (d) (ii) and (iii)
Explanation: Propene has one double bond, while propyne has one triple bond. Hence,
they are unsaturated compounds.
13. Chlorine reacts with saturated hydrocarbons at room temperature in the
(a) absence of sunlight
(b) presence of sunlight
(c) presence of water
(d) presence of hydrochloric acid
Ans. (b) Presence of sunlight
Explanation: Chlorine reacts with saturated hydrocarbons in the presence of sunlight and displaces hydrogen atoms one by one.
14. In the soap micelles
(a) the ionic end of soap is on the surface of the cluster while the carbon chain is in the interior of the cluster.
(b) ionic end of soap is in the interior of the cluster and the carbon chain is out of the cluster.
(c) both ionic end and carbon chain are in the interior of the cluster.
(d) both ionic end and carbon chain are on the exterior of the cluster.
Ans. (a) the ionic end of soap is on the surface of the cluster while the carbon chain is in the interior of the cluster.
15. Pentane has the molecular formula C5H12. It has
(a) 5 covalent bonds
(b) 12 covalent bonds
(c) 16 covalent bonds
(d) 17 covalent bonds
Ans. (c) 16 covalent bonds
Explanation: Following is the structural formula of pentane. It shows 16 covalent bonds:
16. Structural formula of benzene is
Ans. (c)
Explanation: Formula of benzene is C6H6. Option (a) and (d) show the same formula. In option c, all the arms of carbon atoms are occupied.
17. Ethanol reacts with sodium and forms two products. These are
(a) sodium ethanoate and hydrogen
(b) sodium ethanoate and oxygen
(c) sodium ethoxide and hydrogen
(d) sodium ethoxide and oxygen
Ans. (c) Sodium ethoxide and hydrogen
Explanation: This reaction can be shown by following equation:
2Na + 2CH3CH2OH → 2CH3CH2ONa + H2
18. The correct structural formula of butanoic acid is
Ans. (d)
Explanation: Formula of butanoic acid is C3H7COOH.
19. Vinegar is a solution of
(a) 50% - 60% acetic acid in alcohol
(b) 5% - 8% acetic acid in alcohol
(c) 5% - 8% acetic acid in water
(d) 50% - 60% acetic acid in water
Ans. (c) 5% - 8% acetic acid in water
20. Mineral acids are stronger acids than carboxylic acids because
(i) mineral acids are completely ionized
(ii) carboxylic acids are completely ionized
(iii) mineral acids are partially ionized
(iv) carboxylic acids are partially ionized
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans. (a) (i) and (iv)
Explanation: Mineral acids are completely ionized but carboxylic acids are partially ionized. Hence, mineral acids are stronger acids than carboxylic acids.
21. Carbon forms four covalent bonds by sharing its four valence electrons with four univalent atoms, e.g. hydrogen. After the formation of four bonds, carbon attains the electronic configuration of
(a) helium
(b) neon
(c) argon
(d) krypton
Ans. (b) Neon
Explanation: Electronic configuration of carbon is 2, 4 and after sharing four electrons from four univalent atoms, its electronic configuration becomes 2, 8 which is same as that of Neon.
22. The correct electron dot structure of a water molecule is
(a) (b)
(c)
(d)
Ans. (c) Explanation: This dot structure shows a complete octet after oxygen shared two electrons with two univalent atoms of hydrogen.
23. Which of the following is not a straight chain hydrocarbon?
Ans. (d)
Explanation: In this option, three carbon atoms are sharing electrons with univalent atoms. In other options, only two carbon atoms are sharing electrons with univalent atoms.
24. Which among the following are unsaturated hydrocarbons?
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Ans. (c) (ii) and (iv)
Explanation: These compounds show double and triple bonds. Hence they are unsaturated hydrocarbons
25. Which of the following does not belong to the same homologous series?
(a) CH4
(b) C2H6
(c) C3H8
(d) C4H8
Ans. (d) C4H8
Explanation: The general formula for this compound is CnH2n, while that of other options is CnH2n+2.
26. The name of the compound CH3— CH2— CHO is
(a) Propanal
(b) Propanone
(c) Ethanol
(d) Ethanal
Ans. (b) Propanone
Explanation: This compound has −CHO as active radical. Hence, one suffix is used.
27. The heteroatoms present in CH3— CH2— O — CH2— CH2Cl are
(i) oxygen
(ii) carbon
(iii) hydrogen
(iv) chlorine
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans. (d) (i) and (iv)
Explanation: Oxygen and chlorine are not among essential components of hydrocarbons.
28. Which of the following represents saponification reaction?
Ans. (d)
Explanation: When ester is treated with an alkali, the reaction gives ethanol and sodium ethanoate. This reaction is called saponification reaction.
29. The first member of alkyne homologous series is
(a) ethyne
(b) ethene
(c) propyne
(d) methane
Ans. (a) Ethyne