NCERT Solution: Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chemical reactions that release energy in the form of heat, light, or sound are called exothermic reactions.
Example: C (g) + O2 (g) → CO2 + Heat Energy
Reactions that absorb energy or require energy in order to proceed are called endothermic reactions.
Example:
heat
N2 + O2 -------> 2NO
Respiration is considered as an exothermic reaction because in respiration oxidation of glucose takes place which produces large amount of heat energy.
C6H12O6 (aq) + 6O2 (g) → 6CO2 (g) + 6H2O (l) + Energy
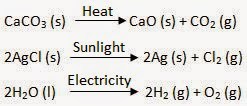
Decomposition reactions are those in which a compound breaks down to form two or more substances. These reactions require a source of energy to proceed. Thus, they are the exact opposite of combination reactions in which two or more substances combine to give a new substance with the release of energy.For Example:
Decomposition Reaction:
heat
CaCO3(s) --------> CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Combination Reaction:
CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq)
In a displacement reaction, a more reactive element replaces a less reactive element from a compound.
For Example: CuSo4 (aq) + Zn (s) → ZnSO4 (aq) + Cu (s)
In a double displacement reaction, two atoms or a group of atoms switch places to form new compounds.
For Example: Na2SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + 2NaCl (aq)
2AgNO3 (aq) + Cu (s) → Cu(NO3)2 (aq) + 2Ag (s)
Silver Nitrate + Copper → Copper Nitrate + Silver
A reaction in which an insoluble solid (called precipitate) is formed is called a precipitation reaction.For Example:
Na2CO3 (aq) + CaCl2 (aq) → CaCO3 (s) + 2NaCl (aq)
Sodium Carbonate + Calcium Chloride → Calcium Carbonate + Sodium Chloride
In this reaction, calcium carbonate is obtained as a precipitate. Hence, it is a precipitation reaction.
Explain the following in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples each.
(a) Oxidation
(b) Reduction
Oxidation Reaction: It is a chemical reaction in which gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen takes place.
For example:
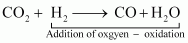
In equation (i), H2is oxidized to H2O and in equation (ii), Cu is oxidised to CuO.
Reduction Reaction: It is a chemical reaction in which loss of oxygen or gain of hydrogen takes place.
For example:
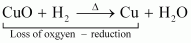
In equation (i), CO2is reduced to CO and in equation (ii), CuO is reduced to Cu.