NCERT Solution: Gravitation
→ An object sink in water if its density is greater than that of water.
→ An object floats in water if its density is less than that of water.
When we weigh our body, an upward force acts on it. This upward force is the buoyant force. As a result, the body gets pushed slightly upwards, causing the weighing machine to show a reading less than the actual value.
The cotton bag is heavier than the iron bar. The cotton bag experiences larger up thrust of air than the iron bar. So, the weighing machine indicates a smaller mass for cotton bag than its actual mass.
If distance r becomes r/2, then the gravitational force will be proportional to
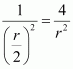
Hence, if the distance is reduced to half, then the gravitational force becomes four times larger than the previous value./p>
All objects fall on ground with constant acceleration, called acceleration due to gravity (in the absence of air resistances). It is constant and does not depend upon the mass of an object. Hence, heavy objects do not fall faster than light objects.
Where,
Mass of Earth, M = 6 x 1024kg
Mass of object, m = 1 kg
Universal gravitational constant, G = 6.7 x 10 - 11Nm2kg - 2
Since the object is on the surface of the Earth, r = radius of the Earth (R)
r= R = 6.4 x 106 m
Gravitational force,
According to the universal law of gravitation, two objects attract each other with equal force, but in opposite directions. The Earth attracts the moon with an equal force with which the moon attracts the earth.
The Earth and the moon experience equal gravitational forces from each other. However, the mass of the Earth is much larger than the mass of the moon. Hence, it accelerates at a rate lesser than the acceleration rate of the moon towards the Earth. For this reason, the Earth does not move towards the moon.