NCERT Solution: Heredity and Evolution
Evolution cannot always be equated with progress or better body designs. Evolution simply creates more complex body designs. However, this does not mean that the simple body designs are inefficient. In fact, bacteria having a simple body design are still the most cosmopolitan organisms found on earth. They can survive hot springs, deep sea, and even freezing environment.
Therefore, bacteria, spiders, fish, and chimpanzees are all different branches of evolution.
A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. The progeny all bore violet flowers but almost half of them were short. This suggests that the genetic make-up of the tall parent can be depicted as
(a) TTWW (b) TTww
(c) TtWW (d) TtWw
ans (c) TtWW
An example of homologous organs is
(a) Our arm and a dog’s fore-leg.
(b) Our teeth and an elephant’s tusks.
(c) Potato and runners of grass.
(d) All of the above.
ans (d) all of the above
In evolutionary terms, we have more in common with
(a) A Chinese school-boy.
(b) A chimpanzee
(c) A spider
(d) A bacterium
ans (a) a Chinese school boy
A study found that children with light-coloured eyes are likely to have parents with light-coloured eyes. On this basis, can we say anything about whether the light eye colour trait is dominant or recessive? Why or why not?
ANSWER:
No, since two copies of traits are inherited from parents, one from mother and the other form father. Unless we know the nature of these two variants of traits we can not tell which is dominant and which is recessive. Recessive traits appear when both the parents contribute recessive allele. From this statement we can only presume are that both parents are contributing recessive allele.
When we classify organism we look for similarities among organism which allows us to group them. Based on these principles we can work out the evolutionary relationship to the species.
Homologous organs are similar in origin (or are embryologically similar) but perform different functions. For example, the forelimbs of humans and the wings of birds look different externally but their skeletal structure is similar. It means that their origin is similar (as wings in birds are modifications of forearm) but functions are different - the wings help in flight whereas human forearm helps in various activities.
Example- fore arm of frog, lizard and bird.
Analogous organs, on the other hand, have different origin but perform similar functions. For example, the wings of a bird and a bat are similar in function but this similarity does not mean that these animals are more closely related. If we carefully look at these structures, then we will find that the wings of a bat are just the folds of skin that are stretched between its fingers whereas the wings of birds are present all along the arm. Therefore, these organs are analogous organs
Wings of birds and wings of insects.
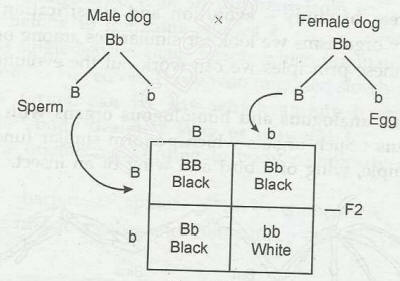
A dog inherits one gene from each of its parents. The dominant gene gets
expressed in the phenotype. For example, in the B series, a dog can be
genetically black or brown.
Let us assume that one parent is homozygous black (BB), while the other parent
is homozygous brown (bb)
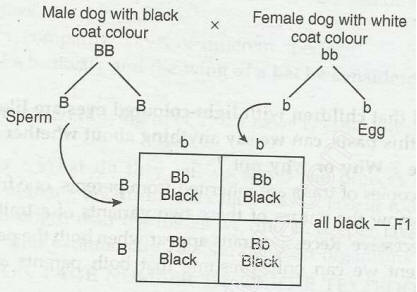
In this case, all the offsprings will be heterozygous (Bb).
Since black (B) is dominant, all the offsprings will be black. However, they
will have both B and b alleles.
If such heterozygous pups are crossed, they will produce 25% homozygous black
(BB), 50% heterozygous black (Bb), and 25% homozygous brown (bb) offsprings.