NCERT Solution: Life Processes
| Transport of materials in xylem | Transport of materials in phloem |
| Xylem tissue helps in the transport of water and minerals. | Phloem tissue helps in the transport of food. |
| Water is transported upwards from roots to all other plant parts. | Food is transported in both upward and downward directions. |
| Transport in xylem occurs with the help of simple physical forces such as transpiration pull. | Transport of food in phloem requires energy in the form of ATP. |
| Alveoli | Nephrons |
| Structure | Structure |
| Alveoli are tiny balloon-like structures present inside the lungs. | Nephrons are tubular structures present inside the kidneys. |
The walls of the alveoli are one cell thick and it contains an extensive network of blood capillaries.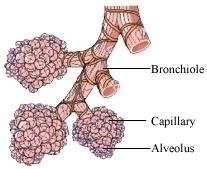 |
Nephrons are made of glomerulus, bowman’s capsule, and a long renal tube.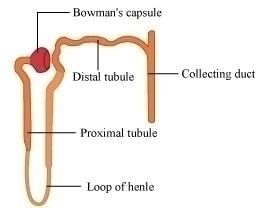 |
| Function | Function |
| The exchange of O2 and CO2 takes place between the blood of the capillaries that surround the alveoli and the gases present in the alveoli. | The blood enters the kidneys through the renal artery. |
| Alveoli are the site of gaseous exchange. | The blood is entered here and the nitrogenous waste in the form of urine is collected by collecting duct.Nephrons are the basic filtration unit. |
1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect?
(a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence of sunlight and chlorophyll
(b) They store carbohydrates in the form of starch
(c) They convert carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight
(d) They constitute the first trophic level in food chains
Ans. (c) They convent carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates in the absence of sunlight.
2. In which of the following groups of organisms, food material is broken down outside the body and absorbed?
(a) Mushroom, green plants, Amoeba
(b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
(c) Paramecium, Amoeba, Cuscuta
(d) Cuscuta, lice, tapeworm
Ans. (b) Yeast, mushroom, bread mould
Explanation: All of them are saprotrophs. In saprotrophic mode of nutrition, food material is broken down outside the body and absorbed.
3. Select the correct statement
(a) Heterotrophs do not synthesise their own food
(b) Heterotrophs utilise solar energy for photosynthesis
(c) Heterotrophs synthesise their own food
(d) Heterotrophs are capable of converting carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates
Ans. (a) Heterotrophs do not synthesise their own food.
Explanation: Heterotrophs depend on other organisms for food.
4. Which is the correct sequence of parts in human alimentary canal?
(a) Mouth →stomach →small intestine →oesophagus →large intestine
(b) Mouth →oesophagus →stomach →large intestine →small intestine
(c) Mouth →stomach →oesophagus →small intestine →large intestine
(d) Mouth →oesophagus →stomach →small intestine →large intestine
Ans. (d) Mouth →oesophagus →stomach →small intestine →large intestine
5. If salivary amylase is lacking in the saliva, which of the following events in the mouth cavity will be affected?
(a) Proteins breaking down into amino acids
(b) Starch breaking down into sugars
(c) Fats breaking down into fatty acids and glycerol
(d) Absorption of vitamins
Ans. (b) Starch breaking down into sugars
Explanation: Salivary amylase converts starch into sugar. Digestion of proteins and fats does not take place in mouth, hence options (a) and (c) are incorrect.
6. The inner lining of stomach is protected by one of the following from hydrochloric acid. Choose the correct one
(a) Pepsin
(b) Mucus
(c) Salivary amylase
(d) Bile
Ans. (b) Mucus
Explanation: Mucus protects the inner lining of stomach from hydrochloric acid.
7. Which part of alimentary canal receives bile from the liver?
(a) Stomach
(b) Small intestine
(c) Large intestine
(d) Oesophagus
Ans. (b) Small intestine
Explanation: Bile from gall bladder goes to small intestine through hepatopancreatic duct.
8. A few drops of iodine solution were added to rice water. The solution turned blueblack in colour. This indicates that rice water contains
(a) complex proteins
(b) simple proteins
(c) fats
(d) starch
Ans. (d) Starch
Explanation: Starch makes a dark blue complex with iodine. This is the most often used test to check the presence of starch in something.
9. In which part of the alimentary canal food is finally digested?
(a) Stomach
(b) Mouth cavity
(c) Large intestine
(d) Small intestine
Ans. (d) Small intestine
Explanation: Partial digestion of food takes place in mouth and stomach. Digestion does not happen in large intestine. It is the small intestine, where digestion is completed.
10. Choose the function of the pancreatic juice from the following
(a) trypsin digests proteins and lipase carbohydrates
(b) trypsin digests emulsified fats and lipase proteins
(c) trypsin and lipase digest fats
(d) trypsin digests proteins and lipase emulsified fats
Ans. (d) Trypsin digests proteins and lipase emulsified fats
Explanation: Trypsin completes the digestion of protein. Lipase digests emulsified fat to convert it into fatty acids and glycerol.
11. When air is blown from mouth into a test-tube containing lime water, the lime water turned milky due to the presence of
(a) oxygen
(b) carbon dioxide
(c) nitrogen
(d) water vapour
Ans. (b) Carbon dioxide
Explanation: Carbon dioxide reacts with limewater Ca(OH)2 to form calcium carbonate which makes the lime water milky.
12. The correct sequence of anaerobic reactions in yeast is
Ans. (d)
Explanation: Breakdown of pyruvate; under anaerobic condition; takes place in
cytoplasm of yeast. Ethanol and carbon dioxide are produced at the end of this
reaction.
13. Which of the following is most appropriate for aerobic respiration?
Ans. (d)
Explanation: In aerobic respiration, breakdown of pyruvate takes place in
mitochondria. Carbon dioxide and water are produced at the end of this reaction.
14. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true about respiration?
(i) During inhalation, ribs move inward and diaphragm is raised
(ii) In the alveoli, exchange of gases takes place i.e., oxygen from alveolar
air diffuses into blood and carbon dioxide from blood into alveolar air
(iii) Haemoglobin has greater affinity for carbon dioxide than oxygen
(iv) Alveoli increase surface area for exchange of gases
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans. (d) (ii) and (iv)
Explanation: Statement (i) is incorrect. During inhalation, ribs move outward
and diaphragm is lowered. Statement (iii) is incorrect because haemoglobin has
greater affinity for oxygen than carbon dioxide.
15. Which is the correct sequence of air passage during inhalation?
(a) Nostrils →larynx →pharynx →trachea →lungs
(b) Nasal passage →trachea →pharynx →larynx →alveoli
(c) larynx →nostrils →pharynx →lungs
(d) Nostrils →pharynx →larynx →trachea →alveoli
Ans. (d) Nostrils →pharynx →larynx →trachea →alveoli
Explanation: Refer to fig 6.9 (NCERT Text book) to see the correct sequence of
organs in human respirator system.
16. During respiration exchange of gases take place in
(a) trachea and larynx
(b) alveoli of lungs
(c) alveoli and throat
(d) throat and larynx
Ans. (b) Alveoli of lungs
Explanation: Trachea and larynx just serve as passage for air. Exchange of gases
takes place in alveoli; where oxygen diffuses into blood and carbon dioxide
comes out of blood.
17. Which of the following statement (s) is (are) true about heart?
(i) Left atrium receives oxygenated blood from different parts of body while
right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from lungs
(ii) Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different body parts while right
ventricle pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs
(iii) Left atrium transfers oxygenated blood to right ventricle which sends it
to different body parts
(iv) Right atrium receives deoxygenated blood from different parts of the body
while left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood to different parts of the body
(a) (i)
(b) (ii)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iii)
Ans. (c) (ii) and (iv)
Explanation: Deoxygenated blood circulates through right part of the heart,
while oxygenated blood circulates through left part of the heart. Atrium
receives blood, while ventricle pumps the blood out.
18. What prevents backflow of blood inside the heart during contraction?
(a) Valves in heart
(b) Thick muscular walls of ventricles
(c) Thin walls of atria
(d) All of the above
Ans. (a) Valves in heart
Explanation: Walls of heart facilitate the pumping action only and have no role
in preventing backflow of blood.
19. Single circulation i.e., blood flows through the heart only once during one
cycle of passage through the body, is exhibited by
(a) Labeo, Chameleon, Salamander
(b) Hippocampus, Exocoetus, Anabas
(c) Hyla, Rana, Draco
(d) Whale, Dolphin, Turtle
Ans. (b) Hippocampus, Exocoetus, Anabas
Explanation: In option �a�; salamander is amphibian, while chameleon is reptile;
and they have three chambered heart. Thus, these animals show partial double
circulation. In option �c� all animals are amphibians.
In option �d� whale is mammal, while turtle is reptile. Mammals have
four-chambered heart and completely double circulation.
20. In which of the following vertebrate group/groups, heart does not pump
oxygenated blood to different parts of the body?
(a) Pisces and amphibians
(b) Amphibians and reptiles
(c) Amphibians only
(d) Pisces only
Ans. (d) Pisces only
Explanation: This happens because of single circulation.
21. Choose the correct statement that describes arteries.
(a) They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under high pressure; collect
blood from different organs and bring it back to the heart
(b) They have thin walls with valves inside, blood flows under low pressure and
carry blood away from the heart to various organs of the body
(c) They have thick elastic walls, blood flows under low pressure; carry blood
from the heart to various organs of the body
(d) They have thick elastic walls without valves inside, blood flows under high
pressure and carry blood away from the heart to different parts of the body.
Ans. (d) They have thick elastic walls without valves inside, blood flows under
high pressure
22. The filtration units of kidneys are called
(a) Ureter
(b) Urethra
(c) Neurons
(d) Nephrons
Ans. (d) Nephrons
Explanation: Due to this, nephron is called the functional unit of Kidney.
23. Oxygen liberated during photosynthesis comes from
(a) water
(b) chlorophyll
(c) carbon dioxide
(d) glucose
Ans. (a) water
Explanation: Splitting of water molecule, results in liberation of oxygen and
hydrogen. Hydrogen is utilized for reduction of carbon dioxide so that
carbohydrate can be made.
24. The blood leaving the tissues becomes richer in
(a) carbon dioxide
(b) water
(c) heamoglobin
(d) oxygen
Ans. (a) carbon dioxide
Explanation: Carbon dioxide accumulates in tissues because of respiration in
cells. Thus, blood leaving the tissues becomes richer in carbon dioxide.
25. Which of the following is an incorrect statement?
(a) Organisms grow with time
(b) Organisms must repair and maintain their structure
(c) Movement of molecules does not take place among cells
(d) Energy is essential for life processes
Ans. (c) Movement of molecules does no take place among cells
Explanation: Movement of molecules is an important aspect of life process and it is necessary that such movements take place among cells.
26. The internal (cellular) energy reserve in autotrophs is
(a) glycogen
(b) protein
(c) starch
(d) fatty acid
Ans. (c) Starch
Explanation: Plants store food in the form of starch.
27. Which of the following equations is the summary of photosynthesis?
(a) 6CO2 + 12H2O → C6H12O6 + 6H2O
(b) 6CO2 + H2O + Sunlight → C6H12O6 + O2 + 6H2O
(c) 6CO2 + 12H2O + Chlorophyll + Sunlight → C6H12O6 + 6O2 + 6H2O
(d) 6CO2 + 12H2O + Chlorophyll + Sunlight → C6H12O6 + 6CO2 + 6H2O
Ans. (c)
Explanation: Option ‘a’ shows correct reaction. But option ‘c’ shows correct reaction as well as other important factors of reaction. Option ‘b’ is not a balanced equation. Option ‘d’ shows carbon dioxide among the products; which is wrong.
28. Choose the event that does not occur in photosynthesis
(a) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll
(b) Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates
(c) Oxidation of carbon to carbon dioxide
(d) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy
Ans. (c) Oxidation of carbon to carbon dioxide
29. The opening and closing of the stomatal pore depends upon
(a) oxygen
(b) temperature
(c) water in guard cells
(d) concentration of CO2 in stomata
Ans. (c) Water in guard cells
Explanation: When water enters the guard cells. they become turgid and facilitate the opening of guard cells. When water comes out of guard cells, they become flaccid and facilitate the closing of guard cells.
30. Choose the forms in which most plants absorb nitrogen
(i) Proteins
(ii) Nitrates and Nitrites
(iii) Urea
(iv) Atmospheric nitrogen
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans. (b) (ii) and (iii)
Explanation: Plants cannot take up atmospheric nitrogen and hence option ‘iv’ is incorrect. Protein is synthesized by plants and hence option ‘i’ is incorrect
31. Which is the first enzyme to mix with food in the digestive tract?
(a) Pepsin
(b) Cellulase
(c) Amylase
(d) Trypsin
Ans. (c) Amylase
Explanation: Amylase is present in saliva; which is secreted in mouth. Hence, this is the first enzyme to mix with food.
32. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) correct?
(i) Pyruvate can be converted into ethanol and carbon dioxide by yeast
(ii) Fermentation takes place in aerobic bacteria
(iii) Fermentation takes place in mitochondria
(iv) Fermentation is a form of anaerobic respiration
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (i) and (iv)
(d) (ii) and (iii)
Ans. (c) (i) and (iv)
Explanation: Fermentation takes place in anaerobes. Fermentation does not take place in mitochondria. Hence, Options (ii) and (iii) are incorrect.
33. Lack of oxygen in muscles often leads to cramps among cricketers. This results due to
(a) conversion of pyruvate to ethanol
(b) conversion of pyruvate to glucose
(c) non-conversion of glucose to pyruvate
(d) conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid
Ans. (d) conversion of pyruvate to lactic acid
Explanation: In case of excess demand of energy in muscles, anaerobic respiration takes place in muscle cells. This results in accumulation of lactic acid in muscles which results in cramps.
34. Choose the correct path of urine in our body
(a) kidney →ureter →urethra →urinary bladder
(b) kidney →urinary bladder →urethra →ureter
(c) kidney →ureters →urinary bladder →urethra
(d) urinary bladder →kidney →ureter →urethra
Ans. (c) kidney →ureters →urinary bladder →urethra
Explanation: Refer to fig: 6.13 (NCERT Text book) for proper sequence of organs in excretory system.
35. During deficiency of oxygen in tissues of human beings, pyruvic acid is converted into lactic acid in the
(a) cytoplasm
(b) chloroplast
(c) mitochondria
(d) golgi body
Ans. (a) cytoplasm
Explanation: Anaerobic respiration takes place in cytoplasm.
(a) The process in plants that links light energy with chemical energy
Ans. Photosynthesis
(b) Organisms that can prepare their own food
Ans. Autotrophs
(c) The cell organelle where photosynthesis occurs
Ans. Chloroplast
(d) Cells that surround a stomatal pore
Ans. Guard cells
(e) Organisms that cannot prepare their own food
Ans. Heterotrophs
(f) An enzyme secreted from gastric glands in stomach that acts on proteins.
Ans. Pepsin
This is an incorrect statement. All plants carry on respiration throughout 24 hours and thus give out carbon dioxide throughout the 24 hours. But photosynthesis happens only in presence of sunlight and oxygen is released during daytime.
When water enters the guard cells, they become turgid. This results in opening of stomatal pore. When water exits from the guard cells, they become flaccid. This results in closing of stomata