NCERT Solution: Light Reflection and Refraction
Image distance, v = −10 cm
According to the lens formula,
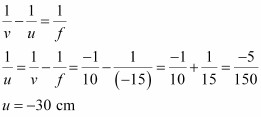
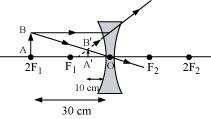
The negative value of u indicates that the object is placed 30 cm in front of the lens. This
is shown in the following ray diagram.
Object distance, u = −10 cm
According to the mirror formula,
v = 6 cm
The positive value of v indicates that the image is formed behind the mirror.

The positive value of magnification indicates that the image formed is virtual
and erect. /p>
The magnification produced by a plane mirror is +1. It shows that the image formed by the plane mirror is of the same size as that of the object. The positive sign shows that the image formed is virtual and erect.
Object distance, u = -20 cm
Object height, h = 5 cm
Radius of curvature, R = 30 cm
Radius of curvature = 2 � Focal length
R = 2f
f = 15 cm
According to the mirror formula,
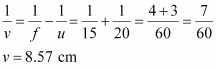
The positive value of v indicates that the image is formed behind the mirror.
The positive value of image height indicates that the image formed is erect.
Therefore, the image formed is virtual, erect, and smaller in size.
Object distance, u = -27 cm
Object height, h = 7 cm
Focal length, f = -18 cm
According to the mirror formula,
The screen should be placed at a distance of 54 cm in front of the given mirror.
The negative value of magnification indicates that the image formed is real.
The negative value of image height indicates that the image formed is inverted.
A concave lens has a negative focal length. Hence, it is a concave lens.
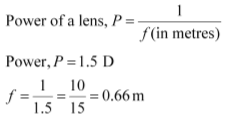
A convex lens has a positive focal length. Hence, it is a convex lens or a converging lens.
1. Which of the following can make a parallel beam of light when light from a
point source is incident on it?
(a) Concave mirror as well as convex lens
(b) Convex mirror as well as concave lens
(c) Two plane mirrors placed at 90� to each other
(d) Concave mirror as well as concave lens
Ans. (a) Concave mirror as well as convex lens
Explanation: When a point source of light is at the focus of a concave mirror or
a convex lens, then emergent rays of light make a parallel beam of light. This
is the reason; concave mirror is used as reflector of headlights.
2. A 10 mm long awl pin is placed vertically in front of a concave mirror. A 5
mm long image of the awl pin is formed at 30 cm in front of the mirror. The
focal length of this mirror is
(a) � 30 cm
(b) � 20 cm
(c) � 40 cm
(d) � 60 cm
Ans. (b) � 20 cm
Explanation: object size h=10 mm, image size h�=5 mm, image distance v= -30 cm,
object
distance =?, f = ?
3. Under which of the following conditions a concave mirror can form an image
larger
than the actual object?
(a) When the object is kept at a distance equal to its radius of curvature
(b) When object is kept at a distance less than its focal length
(c) When object is placed between the focus and centre of curvature
(d) When object is kept at a distance greater than its radius of curvature
Ans. (c) When object is placed between the focus and centre of curvature
Explanation: When object is placed between F and C, an enlarged image is formed
beyond C.
4. Figure 10.1 shows a ray of light as it travels from medium A to medium B.
Refractive index of the medium B relative to medium A is
Ans. (d)
Explanation: Refractive index of medium B relative to medium A can be calculated
as follows:
nBA = Sin i / Sin r
= Sin 300/ Sin 450
= �2
5. A light ray enters from medium A to medium B as shown in Figure 10.2. The
refractive index of medium B relative to A will be
(a) greater than unity
(b) less than unity
(c) equal to unity
(d) zero
Ans. (b) less than unity
Explanation: In this case, the ray of light bends away from normal when it
enters from medium A into medium B. This shows that medium B is optically rarer
than medium A. Hence, speed of light in medium B is more than that in medium A.
So, ratio of speed of light in medium A to speed of light in medium B will be
less than one.
6. Beams of light are incident through the holes A and B and emerge out of
box through the holes C and D respectively as shown in the Figure10.3. Which of
the following could be inside the box?
(a) A rectangular glass slab
(b) A convex lens
(c) A concave lens
(d) A prism
Ans. (d) A prism
Explanation: In this case, incident rays fall perpendicularly on the point of
incidence.
Had it been a glass slab, no refraction would have taken place and rays would
have emerged in the same line as incident rays. In case of convex lens, two
parallel rays would have converged at a point. In case of concave lens, two
parallel rays would have diverged. Hence, it is a prism.
7. A beam of light is incident through the holes on side A and emerges out of
the holes on the other face of the box as shown in the Figure 10.4. Which of the
following could be inside the box?
(a) Concave lens
(b) Rectangular glass slab
(c) Prism
(d) Convex lens
Ans. (a) Concave lens
Explanation: The incident rays are parallel and emergent rays are diverging.
Hence, it is a concave lens (diverging lens).
8. Which of the following statements is true?
(a) A convex lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
(b) A convex lens has �4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
(c) A concave lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
(d) A concave lens has �4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25 m
Ans. (a) A convex lens has 4 dioptre power having a focal length 0.25m
Explanation: The positive sign with the focal length indicates that it is a
convex lens.
9. Magnification produced by a rear view mirror fitted in vehicles
(a) is less than one
(b) is more than one
(c) is equal to one
(d) can be more than or less than one depending upon the position of the object
in front of it
Ans. (a) is less than one
Explanation: Convex mirror is used in rear view mirrors. Convex mirror always
makes smaller images. Hence, magnification produced by rear view mirror is less
than one.