NCERT Solution: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
The needle of a compass is a small magnet. That’s why when a compass needle is brought near a bar magnet, its magnetic field lines interact with that of the bar magnet. Hence, a compass needle gets deflected.
Magnetic field lines of a bar magnet emerge from the north pole and terminate
at the south pole. Inside the magnet, the field lines emerge from the south pole
and terminate at the north pole, as shown in the given figure.
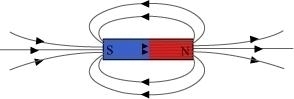
Magnetic Field Lines around a bar magnet
The properties of magnetic lines of force are as follows.
→ Magnetic field lines emerge from the north pole.
→ They merge at the south pole.
→ The direction of field lines inside the magnet is from the south pole to the north pole.
→ Magnetic lines do not intersect with each other.
The two magnetic field lines do not intersect each other because if they do it means at the point of intersect the compass needle is showing two different directions which is not possible.
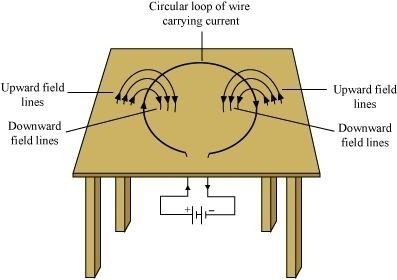
Inside the loop = Pierce inside the table
Outside the loop = Appear to emerge out from the table
For downward direction of current flowing in the circular loop, the direction of
magnetic field lines will be as if they are emerging from the table outside the
loop and merging in the table inside the loop. Similarly, for upward direction
of current flowing in the circular loop, the direction of magnetic field lines
will be as if they are emerging from the table outside the loop and merging in
the table inside the loop, as shown in the given figure.
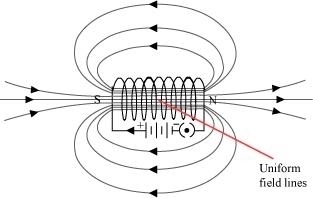
The magnetic field lines inside a current-carrying long straight solenoid are uniform.
Choose the correct option.
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid-carrying current
(a) is zero
(b) decreases as we move towards its end
(c) increases as we move towards its end
(d) is the same at all points
Ans (d) is the same at all points
(d)The magnetic field inside a long, straight, current-carrying solenoid is uniform. It is the same at all points inside the solenoid.
Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer.)
(a) mass
(b) speed
(c) velocity
(d) momentum
Ans (c) velocity and (d) momentum
When a proton enters in a region of magnetic field, it experiences a magnetic force. As a result of the force, the path of the proton becomes circular. Hence, its velocity and momentum change.