NCERT Solution: Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
The essential difference between an AC generator and a DC generator is that
(a) AC generator has an electromagnet while a DC generator has permanent magnet.
(b) DC generator will generate a higher voltage.
(c) AC generator will generate a higher voltage.
(d) AC generator has slip rings while the DC generator has a commutator.
ANS (d) AC generator has slip rings while the DC generator has a commutator.
An AC generator has two rings called slip rings. A DC generator has two half rings called commutator. This is the main difference between both the types of generators.
At the time of short circuit, the current in the circuit
(a) reduces substantially
(b) does not change
(c) increases heavily
(d) vary continuously
ANS (c) increases heavily
When two naked wires of an electric circuit touch each other, the amount of current that is flowing in the circuit increases abruptly. This causes short-circuit.
State whether the following statements are true or false.
(a) An electric motor converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
(b) An electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
(c) The field at the centre of a long circular coil carrying current will be parallel straight lines.
(d) A wire with a green insulation is usually the live wire of an electric supply.
Answer :
(a) False
An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy.
(b) True
A generator is an electric device that generates electricity by rotating a coil in a magnetic field. It works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
(c) True
A long circular coil is a long solenoid. The magnetic field lines inside the solenoid are parallel lines.
(d) False
Live wire has red insulation cover, whereas earth wire has green insulation colour in the domestic circuits.
Three sources of magnetic fields are as follows:
→ Current-carrying conductors
→ Permanent magnets
→ Electromagnets
A solenoid is a long coil of circular loops of insulated copper wire.
Magnetic field lines are produced around the solenoid when a current is allowed
to flow through it. The magnetic field produced by it is similar to the magnetic
field of a bar magnet. The field lines produced in a current-carrying solenoid
is shown in the following figure.
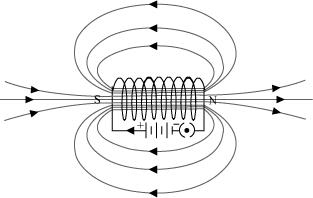
In the above figure, when the north pole of a bar magnet is brought near the end
connected to the negative terminal of the battery, the solenoid repels the bar
magnet. Since like poles repel each other, the end connected to the negative
terminal of the battery behaves as the north pole of the solenoid and the other
end behaves as a south pole. Hence, one end of the solenoid behaves as a north
pole and the other end behaves as a south pole.
The force experienced by a current-currying conductor is the maximum when the direction of current is perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field.
The direction of the magnetic field is vertically downwards. The direction of current is from the front wall to the back wall because negatively charged electrons are moving from back wall to the front wall. The direction of magnetic force is rightward. Hence, using Fleming’s left hand rule, it can be concluded that the direction of magnetic field inside the chamber is downward.
Principle: It works on the principle of the magnetic effect of current. A current-carrying coil rotates in a magnetic field. The following figure shows a simple electric motor.
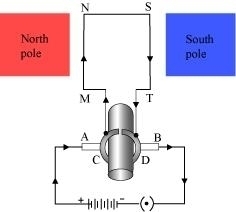
When a current is allowed to flow through the coil MNST by closing the switch, the coil starts rotating anti-clockwise. This happens because a downward force acts on length MN and at the same time, an upward force acts on length ST. As a result, the coil rotates anti-clockwise.
Current in the length MN flows from M to N and the magnetic field acts from left to right, normal to length MN. Therefore, according to Fleming's left hand rule, a downward force acts on the length MN. Similarly, current in the length ST flows from S to T and the magnetic field acts from left to right, normal to the flow of current. Therefore, an upward force acts on the length ST. These two forces cause the coil to rotate anti-clockwise.
After half a rotation, the position of MN and ST interchange. The half-ring D comes in contact with brush A and half-ring C comes in contact with brush B. Hence, the direction of current in the coil MNST gets reversed.
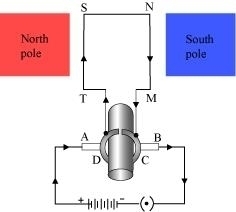
The current flows through the coil in the direction TSNM. The reversal of current through the coil MNST repeats after each half rotation. As a result, the coil rotates unidirectional. The split rings help to reverse the direction of current in the circuit. These are called the commutator.