NCERT Solution: Metals and Non-metals
Iron and aluminium will displace hydrogen from dilute acids as they more reactive then hydrogen. Mercury and copper cannot displace hydrogen from dilute acids as they are less reactive than hydrogen.
In the electrolytic refining of a metal M:
Anode → Impure metal M
Cathode → Thin strip of pure metal M
Electrolyte → Solution of salt of the metal M
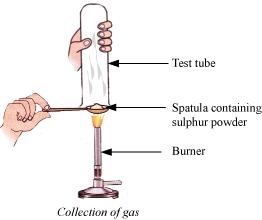
(a)
(i) There will be no action on dry litmus paper.
(ii) The colour of litmus paper will turn red because sulphur is a non-metal and the oxides of non-metal are acidic in nature.
(b) S (s) + O2(g) → SO2 (g)
Two ways to prevent the rusting of iron are:
→ Oiling, greasing, or painting: By applying oil, grease, or paint, the surface becomes water proof and the moisture and oxygen present in the air cannot come into direct contact with iron. Hence, rusting is prevented.
→ Galvanisation:An iron article is coated with a layer of zinc metal, which prevents the iron to come in contact with oxygen and moisture. Hence, rusting is prevented.
When non-metals are combined with oxygen then neutral or acidic oxides are formed. Examples of acidic oxides are NO2, SO2 and examples of neutral oxides are NO, CO etc.
(a) Platinum, gold, and silver are used to make jewellery because they are very lustrous. Also, they are very less reactive and do not corrode easily.
(b) Sodium, potassium, and lithium are very reactive metals and react very vigorously with air as well as water.Therefore, they are kept immersed in kerosene oil in order to prevent their contact with air and moisture.
(c) Though aluminium is a highly reactive metal, it is resistant to corrosion. This is because aluminium reacts with oxygen present in air to form a thin layer of aluminium oxide. This oxide layer is very stable and prevents further reaction of aluminium with oxygen. Also, it is light in weight and a good conductor of heat. Hence, it is used to make cooking utensils.
(d) Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction because metals can be easily extracted from their oxides rather than from their carbonates and sulphides.
Copper reacts with moist carbon dioxide in air to form copper carbonate and as a result, copper vessel loses its shiny brown surface forming a green layer of copper carbonate. The citric acid present in the lemon or tamarind neutralises the basis copper carbonate and dissolves the layer. That is why, tarnished copper vessels are cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice to give the surface of the copper vessel its characteristic lustre.
| Metal | Non Metals |
| Metals are electropositive. | Non-metals are electronegative. |
| They react with oxygen to form basic oxides. 4Na + O2 -> 2Na2O These have ionic bonds |
They react with oxygen to form acidic or neutral oxides. C + O2 -> CO2 These have covalent bonds. |
| They react with water to form oxides and
hydroxides. Some metals react with cold water, some with hot water, and
some with steam. 4Na + O2 -> 2NaOH + H2 |
They do not react with water. |
| They react with dilute acids to form a salt and evolve hydrogen gas. However, Cu, Ag, Au, Pt, Hg do not react. | They do not react with dilute acids. These are not capable of replacing hydrogen. |
| They react with the salt solution of metals.
Depending on their reactivity, displacement reaction can occur. CuSO4 + Zn -> ZnSO4 + Cu |
These react with the salt solution of non-metals. |
| They act as reducing agents (as they can easily
lose electrons). Na -> Na + + e- |
These act as oxidising agents (as they can gain electrons). Cl2 + 2e- --> 2Cl- |