NCERT Solution: Tissues
Complete the table:
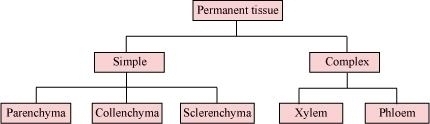
1. Which of the following tissues has dead cells?
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Sclerenchyma
(c) Collenchyma
(d) Epithelial tissue
Ans. (b) Sclerenchyma
Explanation: Sclerenchyma is entirely composed of dead cells. Tissues in others options are composed of live cells only.
2. Find out incorrect sentence
(a) Parenchymatous tissues have intercellular spaces
(b) Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners
(c) Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues
(d) Meristematic tissues, in its early stage, lack vacuoles
Ans. (c) Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues
Explanation: Meristematic tissues are not permanent tissues and hence option ‘c’ is incorrect statement.
3. Girth of stem increases due to
(a) apical meristem
(b) lateral meristem
(c) intercalary meristem
(d) vertical meristem
Ans. (b) lateral meristem
Explanation: Other meristems in options facilities growth in length, while lateral meristem facilities growth in girth.
4. Which cell does not have perforated cell wall?
(a) Tracheids
(b) Companion cells
(c) Sieve tubes
(d) Vessels
Ans. (b) Companion cells
Explanation: Perforated cell walls in cells (options a, c and d) are necessary to make channels for transport of water. Moreover, companion cells are live cells and hence do not have perforated cell wall.
5. Intestine absorbs the digested food materials. What type of epithelial cells are
responsible for that?
(a) Stratified squamous epithelium
(b) Columnar epithelium
(c) Spindle fibres
(d) Cuboidal epithelium
Ans. (b) Columnar epithelium
Explanation: Epithelium in option ‘a’ is present in skin and that in option ‘d’ is meant for structural support. Columnar epithelium facilities absorption. Tissue in option ‘c’ is not a type of epithelium.
6. A person met with an accident in which two long bones of hand were dislocated. Which among the following may be the possible reason?
(a) Tendon break
(b) Break of skeletal muscle
(c) Ligament break
(d) Areolar tissue break
Ans. (c) Ligament break
Explanation: Ligaments join a bone to another bone and hence ligament break can result in dislocation.
7. While doing work and running, you move your organs like hands, legs etc. Which among the following is correct?
(a) Smooth muscles contract and pull the ligament to move the bones
(b) Smooth muscles contract and pull the tendons to move the bones
(c) Skeletal muscles contract and pull the ligament to move the bones
(d) Skeletal muscles contract and pull the tendon to move the bones
Ans. (d) Skeletal muscles contract and pull the tendon to move the bones
Explanation: Skeletal muscles are responsible for voluntary movement and hence movement in hand is facilitated by contraction or relaxation in skeletal muscles. A tendon joins a bone to a muscle; so, option ‘d’ is correct.
8. Which muscles act involuntarily?
(i) Striated muscles
(ii) Smooth muscles
(iii) Cardiac muscles
(iv) Skeletal muscles
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Ans. (b) (ii) and (iii)
Explanation: Skeletal muscles are voluntary. They are also striated. Smooth muscles and cardiac muscles are involuntary.
9. Meristematic tissues in plants are
(a) localised and permanent
(b) not limited to certain regions
(c) localised and dividing cells
(d) growing in volume
Ans. (c) localised and dividing cells
Explanation: Cells of meristematic tissue are dividing cells. Meristematic tissue is present only in those parts which needs to grow.
10. Which is not a function of epidermis?
(a) Protection from adverse condition
(b) Gaseous exchange
(c) Conduction of water
(d) Transpiration
Ans. (c) Conduction of water
Explanation: Conduction of water is a function of xylem and not of epidermis.
11. Select the incorrect sentence
(a) Blood has matrix containing proteins, salts and hormones
(b) Two bones are connected with ligament
(c) Tendons are non-fibrous tissue and fragile
(d) Cartilage is a form of connective tissue
Ans. (c) Tendons are non-fibrous tissue and fragile
Explanation: Tendons are fibrous tissue and are highly elastic and strong.
12. Cartilage is not found in
(a) nose
(b) ear
(c) kidney
(d) larynx
Ans. (c) kidney
Explanation: Kidney is composed of different kinds of epithelial tissues.
13. Fats are stored in human body as
(a) cuboidal epithelium
(b) adipose tissue
(c) bones
(d) cartilage
Ans. (b) adipose tissue
Explanation: Another name of adipose tissue is fat tissue.
14. Bone matrix is rich in
(a) fluoride and calcium
(b) calcium and phosphorus
(c) calcium and potassium
(d) phosphorus and potassium
Ans. (b) calcium and phosphorus
Explanation: Bone cells are embedded in a hard matrix which is composed of calcium and phosphorus.
15. Contractile proteins are found in
(a) bones
(b) blood
(c) muscles
(d) cartilage
Ans. (c) muscles
Explanation: Muscles have the ability of contraction and hence contractile proteins are found in them.
16. Voluntary muscles are found in
(a) alimentary canal
(b) limbs
(c) iris of the eye
(d) bronchi of lungs
Ans. (b) limbs
Explanation: movement of organs in other options is not under our conscious control. Hence, voluntary muscles are not found in them.
17. Nervous tissue is not found in
(a) brain
(b) spinal cord
(c) tendons
(d) nerves
Ans. (c) tendons
18. Nerve cell does not contain
(a) axon
(b) nerve endings
(c) tendons
(d) dendrites
Ans. (c) tendons
Explanation: Tendon is a type of connective tissue, while nerve cells compose the nervous tissue.
19. Which of the following helps in repair of tissue and fills up the space inside the organ?
(a) Tendon
(b) Adipose tissue
(c) Areolar
(d) Cartilage
Ans. (c) Areolar
Explanation: Areolar tissue fills the space inside the organ, supports internal organs and helps in repair of tissue.
20. The muscular tissue which function throughout the life continuously without fatigue is
(a) skeletal muscle
(b) cardiac muscle
(c) smooth muscle
(d) voluntary muscle
Ans. (b) cardiac muscle
Explanation: This is the reason; our heart keeps on pumping the blood throughout the life. Other types of muscles work as and when required because they do not need to work continuously.
21. Which of the following cells is found in the cartilaginous tissue of the body?
(a) Mast cells
(b) Basophils
(c) Osteocytes
(d) Chondrocytes
Ans. (d) Chondrocytes
Explanation: Mast cells are found in areolar tissue, basophils are found in blood and osteocytes are found in bone.
22. The dead element present in the phloem is
(a) companion cells
(b) phloem fibres
(c) phloem parenchyma
(d) sieve tubes
Ans. (b) phloem fibres
23. Which of the following does not lose their nucleus at maturity?
(a) Companion cells
(b) Red blood cells
(c) Vessel
(d) Sieve tube cells
Ans. (a) Companion cells
24. In desert plants, rate of water loss gets reduced due to the presence of
(a) cuticle
(b) stomata
(c) lignin
(d) suberin
Ans. (a) cuticle
Explanation: Cuticle works as protective layer to minimize the effect of heat. Thus, cuticle helps in reducing water loss in desert plants.
25. A long tree has several branches. The tissue that helps in the sideways conduction of water in the branches is
(a) collenchyma
(b) xylem parenchyma
(c) parenchyma
(d) xylem vessels
Ans. (d) xylem vessels
Explanation: Collenchyma has no role in transport of water. Parenchyma is a supportive tissue and has nothing to do with conduction of water.
26. If the tip of sugarcane plant is removed from the field, even then it keeps on growing in length. It is due to the presence of
(a) cambium
(b) apical meristem
(c) lateral meristem
(d) intercalary meristem
Ans. (d) intercalary meristem
Explanation: Intercalary meristem facilities the longitudinal growth of internode and thus a sugarcane plant keeps on growing even in the absence of apical meristem.
27. A nail is inserted in the trunk of a tree at a height of 1 metre from the ground level. After 3 years the nail will
(a) move downwards
(b) move upwards
(c) remain at the same position
(d) move sideways
Ans. (c) remain at the same position
Explanation: Longitudinal growth in stem takes place at the top. So, portion below the apical meristem will remain at a constant level even after growth.
28. Parenchyma cells are
(a) relatively unspecified and thin walled
(b) thick walled and specialised
(c) lignified
(d) none of these
Ans. (a) relatively unspecified and thin walled
Explanation: Parenchyma is simplest among simple tissues. Hence, cells are thin-walled and relatively unspecified.
29. Flexibility in plants is due to
(a) collenchyma
(b) sclerenchyma
(c) parenchyma
(d) chlorenchyma
Ans. (a) collenchyma
Explanation: Collenchyma provides rigidity with some flexibility. This is possible because of thickening of cells at corners
30. Cork cells are made impervious to water and gases by the presence of
(a) cellulose
(b) lipids
(c) suberin
(d) lignin
Ans. (c) suberin
31. Survival of plants in terrestrial environment has been made possible by the presence of
(a) intercalary meristem
(b) conducting tissue
(c) apical meristem
(d) parenchymatous tissue
Ans. (b) conducting tissue
Explanation: It is because of conducing tissues that plants are able to take up water from soil. Thus, plants could be able to survive in terrestrial environment where availability of water can be a major issue.
32. Choose the wrong statement
(a) The nature of matrix differs according to the function of the tissue
(b) Fats are stored below the skin and in between the internal organs
(c) Epithelial tissues have intercellular spaces between them
(d) Cells of striated muscles are multinucleate and unbranched
Ans. (c) Epithelial tissues have intercellular spaces between them
Explanation: Epithelial tissues do not have intercellular spaces between them, rather cells are tightly fit together to make a continuous sheet.
33. The water conducting tissue generally present in gymnosperm is
(a) vessels
(b) sieve tube
(c) tracheids
(d) xylem fibres
Ans. (c) tracheids
Explanation: Sieve tubes are present in phloem and hence have no role in transport of water. Xylem fibres provides structural rigidity and have no role in conduction of water. Vessels are generally absent in gymnosperms.
Fat acts as subcutaneous insulation of body for thermoregulation.
Ans. a�(v); b�(iv); c�(iii); d�(i); e�(ii); f�(vi);
Ans. a�(i); b�(ii); c�(iv); d�(iii); e�(v);
Transpiration takes place through stomata. Water vapour comes out of leaves during transpiration. When a potted plant is covered with a glass jar, water vapour (coming out becomes of transpiration) condenses on the wall of glass jar and hence it appears as fine droplets.