Motion A body is dropped from certain height from a uniformly ascending balloon.
The correct graph showing variation of velocity with time for body is :
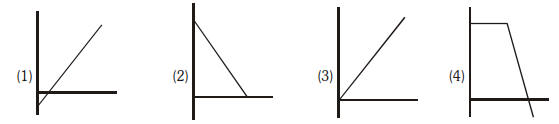
| A. | Option 1 |
| B. | Option 2 |
| C. | Option 3 |
| D. | Option 4 |
|
Option: 1 Solution : -. |
Motion
A ball is thrown vertically upwards. Which of the following plot represents the velocity time graph of the ball during its flight, if the air resistance is not ignored ?
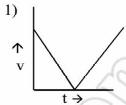
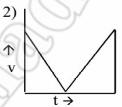
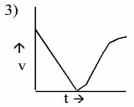
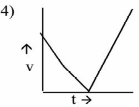
| A. | Option 1 |
| B. | Option 2 |
| C. | Option 3 |
| D. | Option 4 |
|
Option: 3 Solution : -. |
Motion The correct velocity-time graph for zero acceleration is:
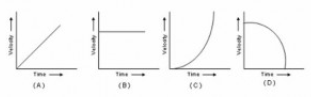
(1) Graph-D
(2) Graph-A
(3) Graph-C
(4) Graph-B
| A. | Option 1 |
| B. | Option 2 |
| C. | Option 3 |
| D. | Option 4 |
|
Option: 4 Solution : -. |
Motion The area under a velocity-time graph is represented by the unit:
(1) m
(2) m-1
(3) m3
(4) m2
| A. | Option 1 |
| B. | Option 2 |
| C. | Option 3 |
| D. | Option 4 |
|
Option: 1 Solution : -. |
Motion What is the slope of distance-time graph when object is at rest?
(1)
Decreases continuously
(2) Zero
(3)
Increases continuously
(4)
One
| A. | Option 1 |
| B. | Option 2 |
| C. | Option 3 |
| D. | Option 4 |
|
Option: 2 Solution : -. |
Motion The displacement covered by a seconds’ hand of radius r in a clock after
one revolution is:
(1) 360 degree
(2) zero
(3) 3r
(4) 2r
| A. | Option 1 |
| B. | Option 2 |
| C. | Option 3 |
| D. | Option 4 |
|
Option: 2 Solution : -. |
Motion
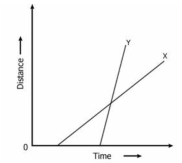
The figure above shows distance-time graphs of two objects X and Y. Which object
is mov ing
with greater speed?
(1)
Both objects are at rest
(2)
Both objects are moving with same speed
(3)
Object Y
(4)
Object X
| A. | Option 1 |
| B. | Option 2 |
| C. | Option 3 |
| D. | Option 4 |
|
Option: 3 Solution : -. |
Motion If car A is at 40 km/h and car B is at 10 km/h in the opposite direction,
what is the velocity of the car A relative to the car B?
(1)
20 km/h
(2)
50 km/h
(3)
10 km/h
(4)
40 km/h
| A. | Option 1 |
| B. | Option 2 |
| C. | Option 3 |
| D. | Option 4 |
|
Option: 2 Solution : -. |
Motion Area under a v – t graph represents a physical quantity which has the unit:
(1) m2
(2) m / s
(3) m / s2
(4) m
| A. | Option 1 |
| B. | Option 2 |
| C. | Option 3 |
| D. | Option 4 |
|
Option: 4 Solution : -. |