Triangles
The ratio of the length of a side of an equilateral triangle and its height is:
(1) 2 : 1
(2) 1 : 2
(3) 2 : √3
(4) √3 : 2
| A. | Option 1 |
| B. | Option 2 |
| C. | Option 3 |
| D. | Option 4 |
|
Option: 3 Solution : -. |
Triangles
In the followign figure QT perpendicular to PR and QS = PS. If <TQR = 40° and <RPS = 20° then value of x is :
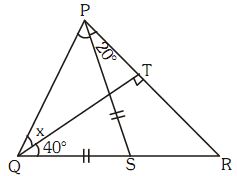
1) 80°
2) 25°
3) 15°
4) 35°
| A. | Option 1 |
| B. | Option 2 |
| C. | Option 3 |
| D. | Option 4 |
|
Option: 3 Solution : -. |
Triangles
ABC and BDE are two equilateral triangles such that D is the mid point of BC. AE intersects BC in F. Then ar (BDE) is equal to
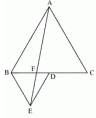
1) 2ar (ABC)
2) 1/4ar (ABC)
3) 1/2ar (ABC)
4) ar (ABC)
| A. | Option 1 |
| B. | Option 2 |
| C. | Option 3 |
| D. | Option 4 |
|
Option: 2 Solution : -. |
Triangles
In an equilateral triangle ABC if AD ꓕ BC, then:
(1) 2AB2 = 2AD2
(2) 4AB2 = 3AD2
(3) 3AB2 = 4AD2
(4) 2AB2 + 2AD2
| A. | Option 1 |
| B. | Option 2 |
| C. | Option 3 |
| D. | Option 4 |
|
Option: 3 Solution : -. |
Triangles
The hypotenuse of a right triangle is 10cm and radius of the inscribed circle is 1 cm. The perimeter of the triangle is:
(1) 15 cm
(2) 22 cm
(3) 24 cm
(4) 18 cm
| A. | Option 1 |
| B. | Option 2 |
| C. | Option 3 |
| D. | Option 4 |
|
Option: 2 Solution : -. |